Investing in dividends has long been a reliable strategy for building wealth over time. However, the allure of high yields can be a tempting path that often leads investors into a dangerous territory. In this article, we’ll explore the risks associated with chasing high yields in dividend investing and discuss strategies for maintaining a balanced and sustainable portfolio.
The Danger Of Chasing High Yields in Dividend Investing
The Allure of High Yields
Many investors are drawn to high-yield stocks due to the promise of substantial returns. The idea of earning a significant income from dividends is undoubtedly appealing, especially in a world where interest rates on traditional savings are often minimal. However, it’s essential to unpack the myths surrounding high yields to make informed investment decisions.
Risks Associated with Chasing High Yields
Unsustainable Yields
One of the primary risks associated with chasing high yields is the potential for those yields to be unsustainable. Companies may offer high dividends to attract investors, but if the underlying fundamentals of the business are weak, it may not be able to maintain those payouts in the long run. Investors should carefully evaluate a company’s financial health, earnings, and cash flow to ensure the sustainability of dividend payments.
Financial Health of the Company
High-yield stocks are often associated with companies facing financial challenges. These companies may be using dividends as a way to attract investors despite struggling with debt, declining profits, or other financial difficulties. Investing in such companies can expose investors to the risk of dividend cuts or even bankruptcy.
Market Volatility
High-yield stocks are often more sensitive to market fluctuations. Economic downturns or industry-specific challenges can impact these companies more severely, leading to a decline in stock prices. Investors relying heavily on high-yield dividends may face significant capital losses during market downturns.
Dividend Cuts
Companies experiencing financial distress may be forced to cut or eliminate dividend payments to preserve capital. Investors relying on these dividends for income may find their cash flow disrupted, leading to financial challenges. A sudden dividend cut can also result in a sharp decline in the stock price, compounding the impact on investors.
Limited Growth Potential
Companies offering high dividends may allocate a significant portion of their earnings to these payouts, leaving less capital for reinvestment in the business. This can hinder the company’s growth prospects and limit its ability to capitalize on new opportunities. As a result, investors may miss out on potential capital appreciation.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
High-yield stocks are often sensitive to changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, income-focused investors may shift their capital to fixed-income securities offering higher yields, leading to a decline in the demand for high-yield stocks. This can result in lower stock prices and negatively impact the total return for investors.
Lack of Diversification
Overemphasizing high-yield stocks in a portfolio can lead to a lack of diversification. Concentrating investments in a specific sector or type of company increases vulnerability to sector-specific risks. Diversifying across various industries and investment types can help mitigate risks and enhance overall portfolio stability.
Importance of Due Diligence
Dividend investing, a strategy favored by many seeking a steady income stream, relies on the careful selection of stocks with reliable dividend payouts. However, the key to success in this investment approach lies in the thorough practice of due diligence. Due diligence is the meticulous examination and evaluation of potential investments to ensure they align with an investor’s goals and risk tolerance. In the realm of dividend investing, this process becomes particularly critical.
Sustainability of Dividend Payouts
Due diligence helps investors assess the sustainability of dividend payments. By scrutinizing a company’s financial statements, cash flow, and earnings history, investors can gain insights into whether the company can consistently meet its dividend obligations. Understanding the financial health of a company is paramount to avoid unpleasant surprises such as unexpected dividend cuts.
Evaluation of Company Fundamentals
Thorough due diligence involves a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s fundamentals. This includes analyzing its competitive position, market share, management team, and growth prospects. A company with strong fundamentals is more likely to weather economic downturns and continue its dividend payouts, providing investors with a reliable income stream.
Historical Dividend Performance
Examining a company’s historical dividend performance is a crucial aspect of due diligence. Investors should assess whether a company has a consistent track record of paying dividends and if there have been any instances of dividend cuts. This historical perspective can offer valuable insights into the company’s commitment to returning value to shareholders.
Sector and Industry Analysis
Due diligence extends to understanding the broader economic environment and specific industry dynamics. Certain sectors may be more resilient to economic downturns, while others may face greater challenges. A well-rounded understanding of the industry landscape can help investors make informed decisions and avoid exposure to sectors with heightened risks.
Dividend Yield in Context
While a high dividend yield can be attractive, due diligence involves putting this metric into context. Investors should consider the company’s overall financial health, earnings growth, and payout ratio. A high yield may indicate an undervalued stock, but it could also signal a riskier investment. Due diligence allows investors to make informed decisions based on a holistic view of the company’s financial picture.
Economic and Market Trends
Due diligence extends beyond individual companies to encompass macroeconomic factors and market trends. Understanding the broader economic environment can help investors anticipate potential challenges that may impact dividend-paying stocks. Economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events all play a role in shaping the investment landscape.
Diversification Strategies
Spreading Investments Across Sectors
Diversification is a fundamental strategy in mitigating risks. By spreading investments across different sectors, investors can minimize the impact of poor performance in any single industry.
Balancing High Yield with Stability
Finding a balance between high-yield stocks and more stable, lower-yield investments is key. This approach can provide consistent returns while still offering the potential for increased income.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Gains
Building Wealth Gradually
Dividend investing is a long-term game. Building wealth gradually through consistent, sustainable dividends is more reliable than seeking quick, but potentially fleeting, returns.
Long-term investors in high-yield dividend stocks can capitalize on the benefits of patience. Over an extended period, dividends can compound, leading to a substantial income stream. Additionally, patient investors are better equipped to ride out market volatility, as they focus on the overall health and trajectory of the companies in which they’ve invested rather than reacting to short-term market noise.
Avoiding the Temptation of Quick Returns
The allure of quick returns can be strong, especially in a fast-paced market. However, the danger lies in the potential for substantial losses if high-yield stocks prove to be unsustainable.
Real-Life Examples
Case Studies of Companies with High Yields
Examining real-life examples of companies that experienced both success and failure in high-yield dividends can offer valuable insights for investors.
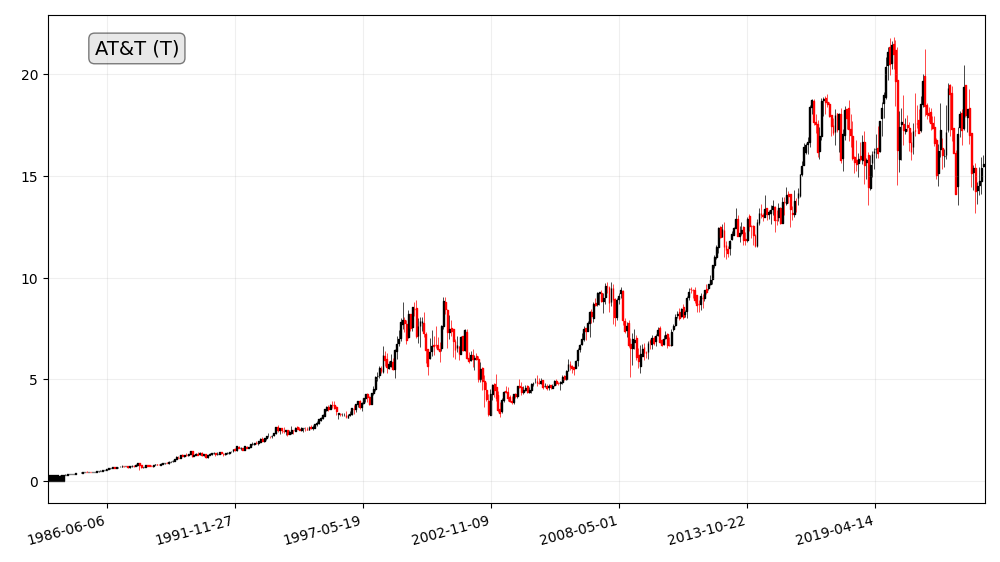
AT&T: A Once-Blue-Chip Stock Now Struggling to Maintain High Dividend Yields
AT&T (T) was once one of the most iconic and successful blue-chip stocks in the world. The company had a long history of paying high dividends, and its stock was a favorite of income investors. However, in recent years, AT&T has struggled to maintain its high dividend yields.
What Went Wrong?
There are a number of factors that have contributed to AT&T’s struggles. For one, the company has been facing increasing competition from other telecom providers, such as Verizon and T-Mobile. These companies have been offering more aggressive pricing and more innovative products and services.
Additionally, AT&T has been burdened by a large debt load. The company took on a significant amount of debt to acquire DirecTV in 2015. However, the DirecTV acquisition has not been as successful as AT&T had hoped.
Finally, AT&T has been impacted by the cord-cutting trend. More and more consumers are canceling their cable TV subscriptions in favor of streaming services like Netflix and Hulu. This has hurt AT&T’s revenue from its video business.
Dividend Cut
In 2022, AT&T was forced to cut its dividend for the first time in over 30 years. The company reduced its quarterly dividend from $0.52 per share to $0.2775 per share. This was a significant cut, and it disappointed many income investors.
Outcomes and Lessons Learned
In 2022, AT&T was forced to cut its dividend for the first time in over 30 years. This was a major setback for the company, and it disappointed many income investors.
Outcomes for High-Yield Dividend Investors
The following are some of the key outcomes for high-yield dividend investors as a result of AT&T’s dividend cut:
- Reduced income: High-yield dividend investors who were invested in AT&T saw their income reduced by over 50% as a result of the dividend cut. This was a significant loss of income for many investors, especially those who were relying on AT&T’s dividends to supplement their retirement income.
- Losses on capital: AT&T’s stock price fell sharply after the dividend cut. As a result, many high-yield dividend investors who were also invested in AT&T’s stock suffered significant capital losses.
Lessons Learned
The following are some important lessons that high-yield dividend investors can learn from AT&T’s dividend cut:
- Not all high-yield dividend stocks are created equal: AT&T was once considered to be a safe and reliable high-yield dividend stock. However, the company’s dividend cut shows that even the best companies can be forced to cut their dividends if they face significant challenges.
- It is important to diversify your portfolio: High-yield dividend investors should diversify their portfolios by investing in a variety of high-yield dividend stocks from different industries. This will help to reduce risk in the event that one company experiences financial difficulties.
- It is important to monitor your investments: High-yield dividend investors should closely monitor their investments and be prepared to sell if a company’s financial situation deteriorates or if the industry outlook changes.
Balancing Risk and Reward
There are a number of things that investors can do to balance the risk and reward of dividend investing, including:
- Invest in quality companies: Investors should focus on investing in quality companies with strong financials and a history of paying dividends.
- Diversify your portfolio: Investors should diversify their portfolio by investing in a variety of dividend stocks from different industries. This will help to reduce risk in the event that one company experiences financial difficulties.
- Reinvest your dividends: When investors reinvest their dividends, they are buying more shares of the company. This can help to reduce risk and increase the potential for capital growth over time.
- Use dividend ETFs: Dividend ETFs are a good way to invest in a basket of dividend stocks without having to pick individual stocks. This can help to reduce risk and make it easier to invest in a diversified portfolio of dividend stocks.
- Consider your investment goals: What are you hoping to achieve with your dividend investments? Are you looking to generate income to supplement your retirement income, or are you looking for capital growth? Once you know your investment goals, you can choose a dividend investing strategy that is right for you.
- Monitor your investments regularly: The investment landscape can change quickly, so it is important to monitor your investments regularly. This includes reviewing the financial performance of the companies you are invested in and the overall market conditions.
- Be prepared to make changes: If the financial performance of a company you are invested in deteriorates, or if the overall market conditions change, you may need to make changes to your dividend investing strategy. This may involve selling some of your investments or investing in different companies.
The Role of Patience
Building Wealth Over Time
At the heart of dividend investing is the concept of building wealth over time. Unlike trading for short-term gains, the patient dividend investor understands that the true value of this strategy unfolds gradually. Patience allows investors to harness the power of compounding, as reinvested dividends contribute to the growth of both the income stream and the overall portfolio.
Enduring Market Volatility
Financial markets are inherently volatile, with prices subject to fluctuations driven by a myriad of factors. Patience serves as a shield against the noise of short-term market movements. Dividend investors, committed to the long game, can weather the storms of volatility with a calm and collected demeanor, focusing on the enduring fundamentals of the companies in which they’ve invested.
Compounding Dividend Income
Dividend investing rewards those who wait. Patience allows investors to benefit from the compounding effect of dividends. As dividends are received and reinvested, the income stream grows, leading to a snowball effect that can significantly enhance the total return on investment over an extended period. This compounding is a testament to the rewards of patient, long-term investing.
Riding Out Economic Cycles
Economic cycles bring both periods of growth and downturns. Patient dividend investors understand that these cycles are part of the natural ebb and flow of the market. By remaining patient and staying committed to their investment strategy, they can ride out economic downturns with the confidence that their well-selected dividend stocks have the resilience to endure and, in some cases, even thrive during challenging times.
Resisting the Urge to Chase Yield
Patience acts as a safeguard against the temptation to chase high yields without due diligence. Investors who are patient in their approach take the time to thoroughly research and evaluate potential investments, ensuring that the companies they choose have sustainable dividend policies and robust financials. This disciplined approach reduces the risk of falling for short-term gains that may prove unsustainable.
Long-Term Financial Goals
Patience aligns with the pursuit of long-term financial goals. Dividend investing is not a get-rich-quick scheme; rather, it is a methodical journey toward financial stability and wealth accumulation. Patient investors are less swayed by the fluctuations of daily market activity, keeping their focus on the horizon and the achievement of their overarching financial objectives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the allure of high yields in dividend investing is undeniable, the associated risks require careful consideration. By conducting thorough due diligence, diversifying portfolios, and balancing risk and reward, investors can navigate the potential pitfalls of chasing high yields and build a sustainable and prosperous financial future.
FAQs
- What is the ideal dividend yield?
- The ideal dividend yield varies based on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. It’s crucial to strike a balance between income generation and risk management.
- How often should I review my dividend portfolio?
- Regular reviews, at least quarterly, are recommended to ensure your portfolio aligns with your financial objectives and market conditions.
- Can high-yield stocks be safe investments?
- High-yield stocks can be safe if chosen wisely. Thorough research and understanding the financial health of the issuing companies are essential.
- How does inflation impact dividend investing?
- Inflation can erode the purchasing power of dividends. Investing in companies with a history of increasing dividends can help counteract the effects of inflation.
- Are there tax implications with high-yield dividends?
- Yes, high-yield dividends may have tax implications. Consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax treatment of your dividend income.