In the world of investing, blue-chip dividend stocks stand out as a reliable and lucrative option for those seeking to grow their wealth. These stocks are often associated with stability, consistent dividends, and a history of outperforming the market. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of blue-chip dividend stocks, exploring what they are, how they work, and why they are an attractive choice for investors.
Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks Overview
Introduction to Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
Blue-chip dividend stocks are the stalwarts of the stock market. They are the shares of well-established, financially stable companies that have a track record of providing consistent dividends to their shareholders. These stocks are often considered the cornerstone of a well-diversified investment portfolio.
What are Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks?
Blue-chip stocks are typically issued by large, renowned companies with a history of stability and reliability. They are household names, and their stocks are often seen as safe havens for investors during turbulent market conditions.
Blue-chip dividend stocks are a subset of these companies that not only offer stability but also regularly distribute a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends. These dividends can provide a steady stream of income for investors, making them an attractive choice, especially for those looking to secure their financial future.
Historical Significance
The term “blue-chip” has an interesting origin. It can be traced back to the world of poker, where blue chips have the highest value. Similarly, in the stock market, blue-chip stocks are considered the most valuable due to their reliability, performance, and dividend-paying history.
Blue-chip dividend stocks have a history dating back many decades, and some have paid dividends without interruption for over a century. This historical significance underscores their resilience and the trust investors have in them.
In the sections that follow, we will explore why investing in blue-chip dividend stocks is a wise choice and how to identify the most promising options.
Why Invest in Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks?
Investing in blue-chip dividend stocks comes with a multitude of benefits. Let’s delve into the key reasons why they are an attractive option for investors.
Stability and Consistency
Blue-chip dividend stocks are renowned for their stability. These companies have weathered numerous economic cycles and have consistently delivered value to their shareholders. This stability provides a sense of security to investors, especially during times of market volatility.
Dividend Income
The primary allure of blue-chip dividend stocks is the regular income they provide. By owning shares in these companies, investors can enjoy a steady stream of dividends, which can be especially appealing for those looking to supplement their income or plan for retirement.
Growth Potential
While blue-chip dividend stocks are often associated with stability, they also offer growth potential. These companies have a proven track record of adapting to changing market conditions and evolving with the times. As a result, their stock prices can appreciate over the long term.
Lower Risk
Investing in blue-chip dividend stocks carries a lower level of risk compared to more speculative investments. These companies are less likely to face financial distress or go out of business, making them a safer bet for risk-averse investors.
In the next section, we will explore how to identify blue-chip dividend stocks and build a portfolio that aligns with your investment goals.
How to Identify Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
Not all large-cap stocks qualify as blue-chip dividend stocks. To make informed investment decisions, it’s essential to know how to identify these gems among the vast sea of investment options.
Financial Stability
One of the core criteria for a blue-chip dividend stock is financial stability. These companies have strong balance sheets, low debt levels, and healthy cash flows. They can weather economic downturns without compromising their dividend payments.
Dividend History
A consistent dividend payment history is a hallmark of blue-chip stocks. Look for companies that have been paying dividends for many years without interruptions. A reliable track record is a strong indicator of a company’s commitment to its shareholders.
Market Capitalization
Most blue-chip dividend stocks are large-cap companies. Market capitalization refers to the total market value of a company’s outstanding shares. Blue-chip stocks are typically among the largest in the market, which adds to their stability.
Industry Leadership
Many blue-chip companies are leaders in their respective industries. Being at the forefront of their sectors, they are better positioned to withstand competition and market challenges.
In the following section, we’ll take a closer look at some popular blue-chip dividend stocks that have captured the attention of investors for decades.
Popular Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
Several blue-chip dividend stocks have maintained their status as dependable investments. Let’s explore a few of these household names and learn why they are favored by investors.
The Coca-Cola Company
Coca-Cola, one of the world’s most recognized brands, is a classic example of a blue-chip dividend stock. Known for its iconic beverages, including the eponymous Coca-Cola, this company has a rich history of rewarding its shareholders with dividends. Its strong global presence and enduring popularity have contributed to its status as a stable investment option.
Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson, a global healthcare conglomerate, is another blue-chip dividend stock that has earned its reputation through decades of consistent performance. The company’s diverse portfolio of healthcare products and pharmaceuticals, coupled with its unwavering commitment to its dividend policy, make it a go-to choice for income-oriented investors.
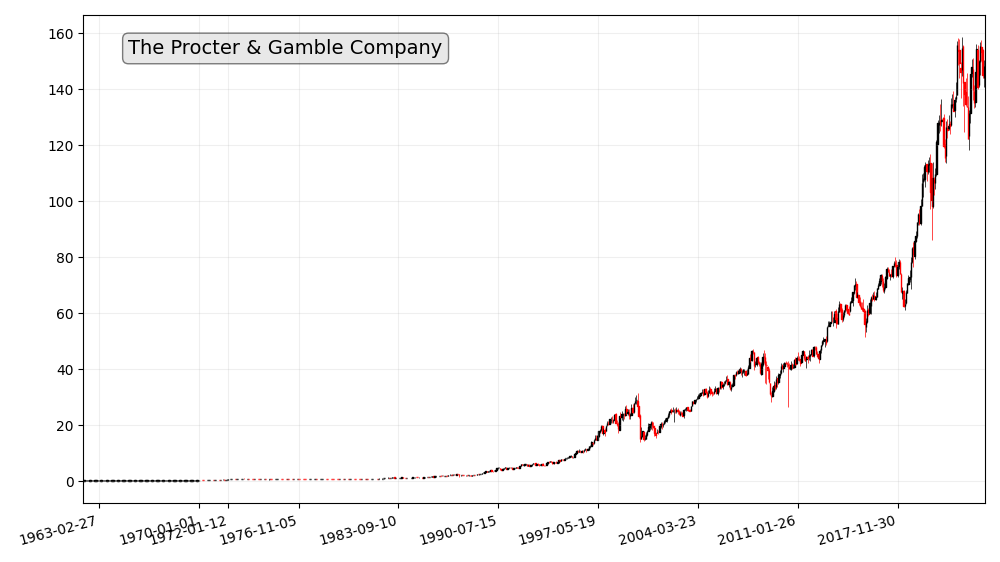
Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble is a consumer goods powerhouse. With a vast array of household brands such as Tide, Crest, and Pampers, the company has maintained its blue-chip status by providing steady dividends and showing resilience in both strong and weak economic climates.
IBM
IBM (International Business Machines Corporation) is a technology giant that has demonstrated its ability to adapt to the ever-changing tech landscape. With a history dating back over a century, IBM is known for not only innovation but also consistent dividend payments, making it a preferred choice for tech-savvy investors.
ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil, a major player in the energy sector, has been a reliable choice for investors seeking exposure to the oil and gas industry. With a commitment to dividend payments and a focus on sustainable practices, the company offers a combination of income and long-term growth potential.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore various strategies for investing in blue-chip dividend stocks, the risks associated with them, and tax considerations.
Investing Strategies with Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
Investors can employ different strategies when considering blue-chip dividend stocks. Here are a few popular approaches:
Buy and Hold
The “buy and hold” strategy involves purchasing blue-chip dividend stocks with the intention of holding them for the long term. This approach relies on the historical stability and growth potential of these stocks to generate returns over time.
Dividend Reinvestment
Investors can choose to reinvest the dividends they receive from blue-chip stocks back into more shares of the same stock. This approach, known as dividend reinvestment, can accelerate wealth accumulation over the years.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy that involves regularly investing a fixed amount of money in blue-chip dividend stocks, regardless of market conditions. This approach can help mitigate the impact of market fluctuations and reduce the risk of making poor investment decisions based on short-term market sentiment.
In the following section, we will discuss the potential risks and challenges associated with investing in blue-chip dividend stocks.
Risks and Challenges
While blue-chip dividend stocks are generally considered safe investments, it’s important to be aware of the risks and challenges associated with them.
Economic Downturns
During severe economic downturns, even blue-chip companies can experience declines in their stock prices. Investors should be prepared for the possibility of temporary setbacks, although these companies often recover over time.
Interest Rate Changes
Blue-chip dividend stocks can be sensitive to changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, the yields on these stocks may become less attractive compared to fixed-income investments, which could lead to a decline in their prices.
Company-Specific Issues
Even the most established companies can face company-specific challenges, such as management issues, product recalls, or legal problems. Investors should stay informed about the companies they invest in and be prepared to adjust their portfolios accordingly.
In the next section, we will delve into the tax implications of investing in blue-chip dividend stocks.
Tax Implications
Investors should consider the tax implications of their investments in blue-chip dividend stocks. Here are some key considerations:
Dividend Taxation
Dividend income is typically subject to taxation. The tax rate can vary depending on the investor’s income level and the jurisdiction they reside in. Understanding the tax treatment of dividends is essential for effective financial planning.
Capital Gains Tax
When selling blue-chip dividend stocks, investors may be subject to capital gains tax on any profits realized. The tax rate for capital gains can also vary based on the holding period and the investor’s tax bracket.
In the subsequent section, we will discuss strategies for building a diversified portfolio of blue-chip dividend stocks.
Building a Blue-Chip Dividend Portfolio
Diversification is a key strategy for reducing risk in your investment portfolio. When building a blue-chip dividend stock portfolio, consider the following factors:
Diversification
Diversify your holdings across different sectors and industries. This spreads the risk and ensures that your portfolio is not overly exposed to the performance of a single sector.
Risk Management
Consider the balance between income and growth when selecting blue-chip dividend stocks. Diversify your portfolio with both high-yield and lower-yield options to create a well-rounded investment strategy.
In the next section, we will discuss the ideal investor profiles for blue-chip dividend stocks and how to maximize returns.
Investor Profile: Who Should Consider Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks?
Blue-chip dividend stocks cater to a variety of investor profiles. Let’s explore who should consider these stocks:
Retirement Planning
Blue-chip dividend stocks can be an excellent choice for those planning their retirement. The regular dividend income can supplement retirement savings and provide financial security in your golden years.
Income-Oriented Investors
Investors seeking consistent income streams can benefit from blue-chip dividend stocks. These stocks offer a reliable source of income, making them suitable for income-oriented investors.
Conservative Investors
For conservative investors who prioritize safety and stability, blue-chip dividend stocks are an ideal choice. They provide an opportunity to invest in well-established companies with a history of reliable performance.
In the following section, we will discuss strategies for maximizing returns with blue-chip dividend stocks.
Strategies for Maximizing Returns
Investors can employ several strategies to make the most of their blue-chip dividend stock investments. Here are some tips:
Timing Your Purchases
Consider market conditions when buying blue-chip stocks. Entering the market during a downturn can provide an opportunity to acquire shares at a more favorable price.
Reinvesting Dividends
Reinvesting dividends can accelerate wealth accumulation. By buying more shares with your dividend income, you can take advantage of compounding returns.
Monitoring Your Portfolio
Stay informed about the companies in your portfolio. Keep track of their financial health, dividend announcements, and overall performance. Make adjustments to your holdings as needed.
In the next section, we will explore the future of blue-chip dividend stocks and the potential trends that may impact them.
The Future of Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
The world of investing is ever-evolving, and blue-chip dividend stocks are not immune to change. Here are some factors that may shape the future of these investments:
Technological Advancements
Technology is a driving force in today’s economy. Blue-chip companies that embrace and adapt to technological advancements are likely to thrive in the coming years.
Market Trends
Keep an eye on market trends and emerging industries. Blue-chip dividend stocks that diversify into new and growing sectors can offer exciting growth opportunities.
In the next section, we will dive into case studies of success stories, showcasing how blue-chip dividend stocks have delivered outstanding results.
Case Studies: Success Stories
Let’s explore two case studies that illustrate the remarkable success of blue-chip dividend stocks:
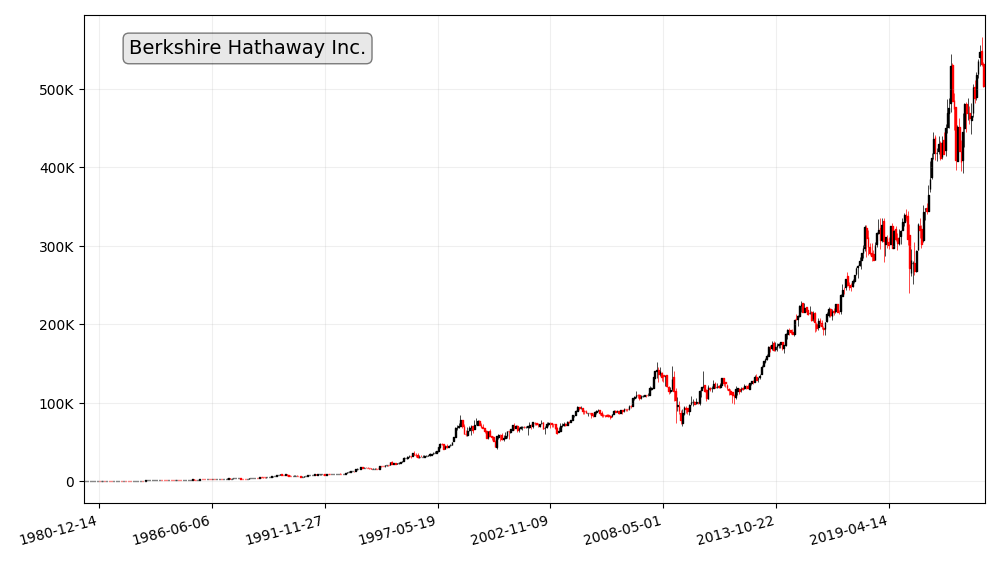
Berkshire Hathaway
Berkshire Hathaway, led by the legendary Warren Buffett, has a long history of value creation for its shareholders. The company’s diversified portfolio, strong management, and prudent investment strategies have made it a standout performer in the world of blue-chip stocks.
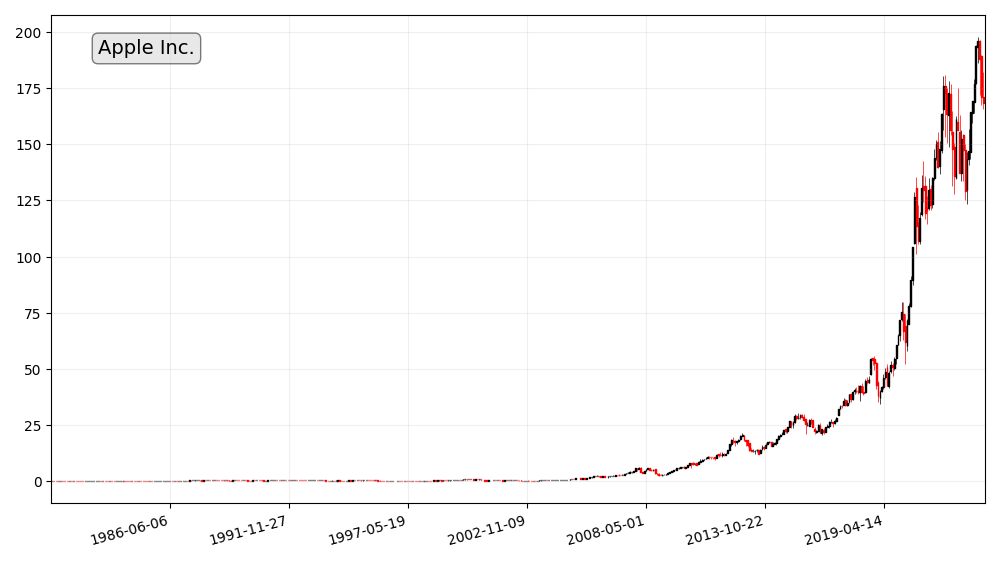
Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. transformed from a niche computer company into one of the world’s most valuable brands. Through its innovative products, consistent revenue growth, and commitment to returning value to shareholders, Apple has become a prime example of a blue-chip stock success story.
In the next section, we will debunk some common myths about blue-chip dividend stocks.
Common Myths About Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
Several misconceptions surround blue-chip dividend stocks. Let’s dispel a couple of common myths:
“Blue-Chip Stocks Are Boring”
While blue-chip stocks are known for stability, they can offer exciting growth potential, especially when they expand into new markets or industries. Their historical performance is a testament to their adaptability and resilience.
“Dividend Stocks Are Only for Income”
Blue-chip dividend stocks are not solely for income-oriented investors. They can also serve as a growth component in a diversified portfolio. Over time, these stocks can appreciate, creating wealth in addition to regular income.
Conclusion: The Timeless Allure of Blue-Chip Dividend Stocks
In conclusion, blue-chip dividend stocks represent a timeless investment option that combines stability, income, and growth potential. They are well-suited for a variety of investor profiles, from those planning for retirement to those seeking consistent income streams. By considering strategies for maximizing returns, managing risks, and staying informed about market trends, investors can make the most of their blue-chip dividend stock investments.
Now, as we wrap up this comprehensive guide, we invite you to explore the possibilities of blue-chip dividend stocks and discover how they can enhance your investment portfolio.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the minimum investment required for blue-chip stocks?
The minimum investment required for blue-chip stocks can vary depending on the stock’s current price. Many blue-chip stocks are well-known for their accessibility, making it possible for investors with different budget sizes to acquire shares.
Can I rely solely on blue-chip stocks for retirement income?
While blue-chip stocks can be a valuable part of your retirement income strategy, it’s generally recommended to have a diversified portfolio that includes a mix of asset classes to spread risk. Relying solely on one type of investment, even blue-chip stocks, may not provide adequate diversification.
How often do blue-chip companies increase their dividends?
Many blue-chip companies have a history of increasing their dividends annually. These increases often match or outpace inflation, helping shareholders maintain their purchasing power over time.
Are blue-chip stocks immune to market volatility?
Blue-chip stocks are not entirely immune to market volatility, but they are generally less susceptible to severe price fluctuations than smaller or riskier investments. Their financial stability and established market positions make them a more secure option.
What should I do if a blue-chip company’s stock price drops significantly?
If a blue-chip company’s stock price experiences a significant drop, it’s essential to assess the reasons behind the decline. Consider your investment goals, time horizon, and portfolio diversification. In some cases, holding onto the stock may be the best course of action, while in others, it may make sense to adjust your investment strategy.
As you embark on your journey into the world of blue-chip dividend stocks, remember to conduct thorough research, stay informed, and consult with a financial advisor if needed. These stocks offer a world of possibilities for those seeking stable, income-generating investments that can stand the test of time.